Reef bleaching leaves little
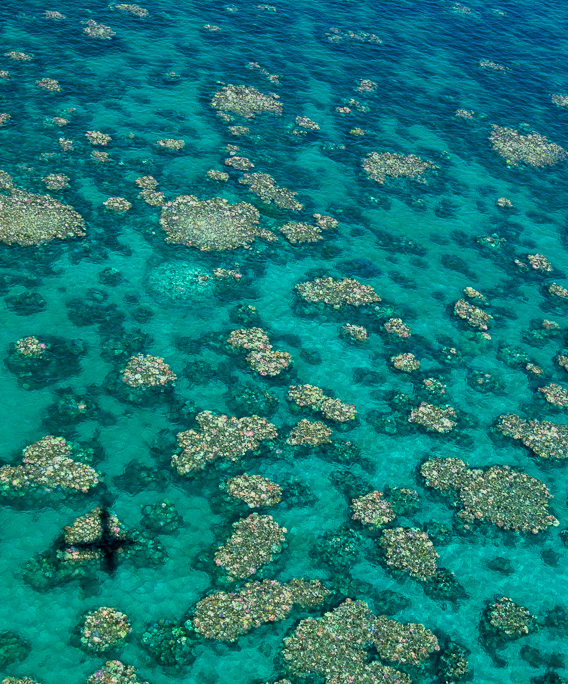 Experts say a rapid swing of climate extremes has left the Great Barrier Reef a bleached ‘checkerboard’.
Experts say a rapid swing of climate extremes has left the Great Barrier Reef a bleached ‘checkerboard’.
A new study reveals the impacts of multiple climate extremes on coral reefs over the past three decades, with only 2 per cent of the Great Barrier Reef escaping bleaching in that time.
The frequency, intensity and scale of climate extremes is changing rapidly due to global warming, including record-breaking marine heatwaves that cause corals to bleach and die.
“We no longer have the luxury of studying individual climate-related events that were once unprecedented or very rare,” says lead author Professor Terry Hughes from the ARC Centre of Excellence for Coral Reef Studies at James Cook University (Coral CoE at JCU).
“Instead, as the world gets hotter, we have to understand the effects of sequences of rapid-fire catastrophes, as well as their combined impacts.”
The Great Barrier Reef is comprised of more than 3,000 individual reefs stretching for 2,300km. The ecosystem supports 65,000 jobs in reef tourism.
The study shows only 2 per cent of the Great Barrier Reef has escaped bleaching since the first event in 1998, then the world’s hottest year on record.
Bleaching is a stress response by overheated corals during heatwaves, where they lose their colour and many struggle to survive. Eighty per cent of reefs bleached severely in 2016, 2017 and 2020.
To better predict how coral reefs will fare under future climate change, Prof Hughes calls for a better understanding of compounding impacts: multiple, climate-driven disturbances that interact with each other over time and space, generating combined effects that cannot be predicted from single events alone.
“For the first time, in 2020, we saw severe bleaching across the whole length of the Reef - in parts of the northern, central and especially the southern region,” Prof Hughes said.
But, he added, each bleaching event has a different geographic footprint. The northern Reef escaped damage in 1998 and 2002 before being the worst-affected region in 2016. The south escaped in 2016 and 2017.
Drawing upon satellite data, the authors of the study also measured the duration and intensity of heat stress the Reef was exposed to each summer, to explain why different parts were affected in each event.
“Heat stress is a very precise predictor of the severity of bleaching every year,” said coauthor Dr Mark Eakin from the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
The scientists found the responses to extreme heat depended on the recent history of bleaching. In 2002 and 2017, it took more heat to reach similar levels of bleaching to those in 1998 and 2016.
“To our surprise, we found the threshold for bleaching was much higher on reefs that had experienced an earlier episode of heat stress,” Dr Eakin said.
“Consequently, the most vulnerable reefs each year were the naïve ones that had not bleached recently.”
Also this week, a separate study shows that recent coral bleaching has reduced the Great Barrier Reef’s recovery potential by 70 per cent.








 Print
Print